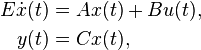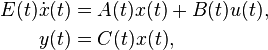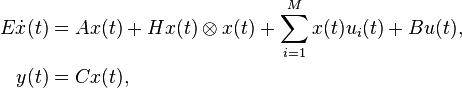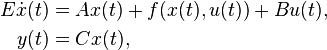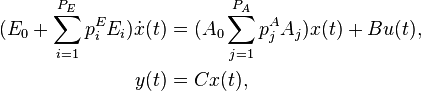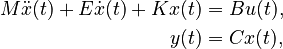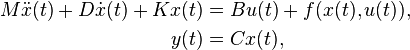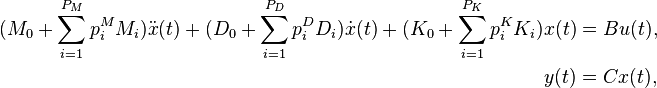m |
|||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
:<math> |
:<math> |
||
\begin{align} |
\begin{align} |
||
| − | M \ddot{x}(t) + |
+ | M \ddot{x}(t) + E \dot{x}(t) + K x(t) &= B u(t), \\ |
y(t) &= C x(t), |
y(t) &= C x(t), |
||
\end{align} |
\end{align} |
||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
<math>M \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}</math>, |
<math>M \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}</math>, |
||
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>E \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}</math>, |
<math>K \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}</math>, |
<math>K \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}</math>, |
||
<math>B \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times M}</math>, |
<math>B \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times M}</math>, |
||
<math>C \in \mathbb{R}^{Q \times N}</math>. |
<math>C \in \mathbb{R}^{Q \times N}</math>. |
||
| − | |||
===Nonlinear Second-Order System=== |
===Nonlinear Second-Order System=== |
||
Revision as of 11:50, 9 February 2019
 Note: This page has not been verified by our editors.
Note: This page has not been verified by our editors.
Benchmark Model Overview
This page outlines the types of models that are used as benchmark systems.
For this general summary we assume an input 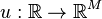 ,
a state
,
a state 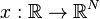 and an output
and an output 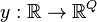 .
.
Linear Time-Invariant System
with:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
Linear Time-Varying System
with:
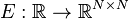 ,
,
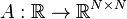 ,
,
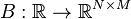 ,
,
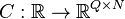 .
.
Quadratic-Bilinear System
with:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
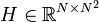 ,
,
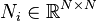 ,
,
 .
.
Nonlinear Time-Invariant System
with:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
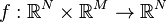 .
.
Affine Parametric Linear Time-Invariant System
with:
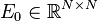 ,
,
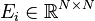 ,
,
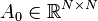 ,
,
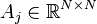 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
Second-Order System
with:
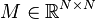 ,
,
 ,
,
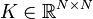 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
Nonlinear Second-Order System
with:
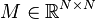 ,
,
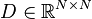 ,
,
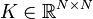 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
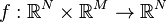 .
.
Affine Parametric Second-Order System
with:
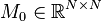 ,
,
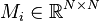 ,
,
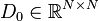 ,
,
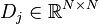 ,
,
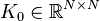 ,
,
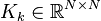 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.