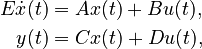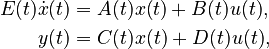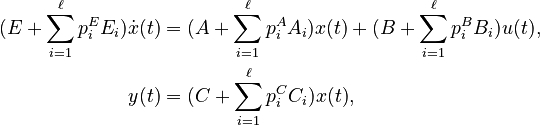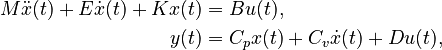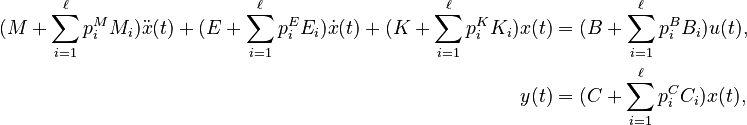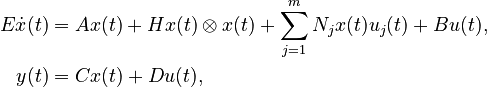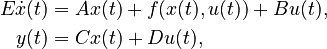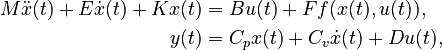(→Affine Parametric Second-Order System: expand section title) |
m (reorder models) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<math>D : \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}^{q \times m}</math>. |
<math>D : \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}^{q \times m}</math>. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | ===Quadratic-Bilinear System (QBS)=== |
||
:<math> |
:<math> |
||
\begin{align} |
\begin{align} |
||
| − | + | (E + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^E_i E_i)\dot{x}(t) &= (A + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^A_i A_i) x(t) + (B + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^B_i B_i)u(t),\\ |
|
| − | + | y(t) &= (C + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^C_i C_i)x(t), |
|
\end{align} |
\end{align} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
with |
with |
||
| − | <math>E \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math> |
+ | <math>E, E_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>; |
| − | <math>A \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math> |
+ | <math>A, A_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>; |
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>B, B_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>; and |
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>C, C_i \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times n}</math>, |
| − | <math> |
+ | for all <math>i = 1, \ldots, \ell</math>. |
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | === |
+ | ===Linear Time-Invariant Second-Order System (LTI-SOS)=== |
:<math> |
:<math> |
||
\begin{align} |
\begin{align} |
||
| − | + | M \ddot{x}(t) + E \dot{x}(t) + K x(t) &= B u(t), \\ |
|
| − | y(t) &= |
+ | y(t) &= C_p x(t) + C_v \dot{x}(t) + D u(t), |
\end{align} |
\end{align} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 73: | Line 71: | ||
with |
with |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<math>E \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
<math>E \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
||
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>K \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
<math>B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>, |
<math>B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>, |
||
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>C_p, C_v \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times n}</math>, |
| − | <math>D \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times m}</math> |
+ | <math>D \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times m}</math>. |
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
:<math> |
:<math> |
||
\begin{align} |
\begin{align} |
||
| − | (E + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^E_i E_i)\dot{x}(t) |
+ | (M + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^M_i M_i)\ddot{x}(t) + (E + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^E_i E_i)\dot{x}(t) + (K + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^K_i K_i)x(t) &= (B + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^B_i B_i) u(t), \\ |
| − | y(t) &= (C + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^C_i C_i)x(t), |
+ | y(t) &= (C + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^C_i C_i) x(t), |
\end{align} |
\end{align} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
with |
with |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<math>E, E_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>; |
<math>E, E_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>; |
||
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>K, K_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>; |
<math>B, B_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>; and |
<math>B, B_i \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>; and |
||
<math>C, C_i \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times n}</math>, |
<math>C, C_i \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times n}</math>, |
||
for all <math>i = 1, \ldots, \ell</math>. |
for all <math>i = 1, \ldots, \ell</math>. |
||
| − | === |
+ | ===Quadratic-Bilinear System (QBS)=== |
:<math> |
:<math> |
||
\begin{align} |
\begin{align} |
||
| − | + | E\dot{x}(t) &= A x(t) + H x(t) \otimes x(t) + \sum_{j=1}^m N_j x(t) u_j(t) + B u(t), \\ |
|
| − | y(t) &= |
+ | y(t) &= Cx(t) + Du(t), |
\end{align} |
\end{align} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 108: | Line 109: | ||
with |
with |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<math>E \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
<math>E \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
||
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>A \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
| + | <math>H \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n^2}</math>, |
||
| + | <math>N_j \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
||
<math>B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>, |
<math>B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>, |
||
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>C \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times n}</math>, |
<math>D \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times m}</math>. |
<math>D \in \mathbb{R}^{q \times m}</math>. |
||
| + | ===Nonlinear Time-Invariant First-Order System (NLTI-FOS)=== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | E\dot{x}(t) &= Ax(t) + f(x(t),u(t)) + Bu(t),\\ |
||
| + | y(t) &= Cx(t) + Du(t), |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>E \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
||
| + | <math>A \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}</math>, |
||
| + | <math>B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}</math>, |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
===Nonlinear Time-Invariant Second-Order System (NLTI-SOS)=== |
===Nonlinear Time-Invariant Second-Order System (NLTI-SOS)=== |
||
| Line 138: | Line 156: | ||
When <math>C_v = 0</math>, we denote <math>C = C_p</math>. |
When <math>C_v = 0</math>, we denote <math>C = C_p</math>. |
||
| − | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | (M + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^M_i M_i)\ddot{x}(t) + (E + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^E_i E_i)\dot{x}(t) + (K + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^K_i K_i)x(t) &= (B + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^B_i B_i) u(t), \\ |
||
| − | y(t) &= (C + \sum_{i=1}^{\ell} p^C_i C_i) x(t), |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | for all <math>i = 1, \ldots, \ell</math>. |
||
Revision as of 20:10, 20 April 2023
Benchmark Model Templates
This page specifies templates for the types of models used as benchmark systems. In particular, the naming schemes established here are used in the corresponding data sets for all benchmarks. For example,  always serves as the name of the component matrix applied to the state
always serves as the name of the component matrix applied to the state 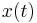 in a linear time-invariant system.
For all models we assume an input
in a linear time-invariant system.
For all models we assume an input 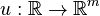 , with components
, with components 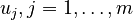 ,
a state
,
a state 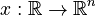 ,
and an output
,
and an output 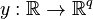 .
For all parametric models, we assume each component has
.
For all parametric models, we assume each component has  parameters; in cases where a component has fewer than
parameters; in cases where a component has fewer than  parameters, the extras are treated as
parameters, the extras are treated as 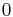 .
Some benchmarks (e.g., Bone Model) have a constant forcing term, in which case, it is assumed that
.
Some benchmarks (e.g., Bone Model) have a constant forcing term, in which case, it is assumed that  is identically
is identically 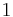 .
.
Linear Time-Invariant First-Order System (LTI-FOS)
with
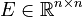 ,
,
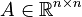 ,
,
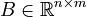 ,
,
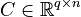 ,
,
 .
.
Linear Time-Varying First-Order System (LTV-FOS)
with
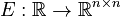 ,
,
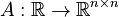 ,
,
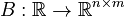 ,
,
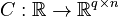 ,
,
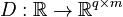 .
.
Affine Parametric LTI-FOS (AP-LTI-FOS)
with
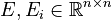 ;
;
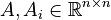 ;
;
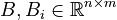 ; and
; and
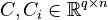 ,
for all
,
for all 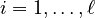 .
.
Linear Time-Invariant Second-Order System (LTI-SOS)
with
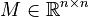 ,
,
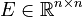 ,
,
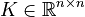 ,
,
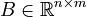 ,
,
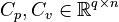 ,
,
 .
.
When 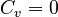 , we denote
, we denote 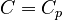 .
.
Affine Parametric LTI-SOS (AP-LTI-SOS)
with
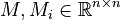 ;
;
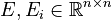 ;
;
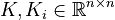 ;
;
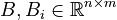 ; and
; and
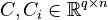 ,
for all
,
for all 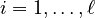 .
.
Quadratic-Bilinear System (QBS)
with
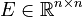 ,
,
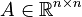 ,
,
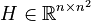 ,
,
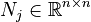 ,
,
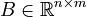 ,
,
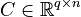 ,
,
 .
.
Nonlinear Time-Invariant First-Order System (NLTI-FOS)
with
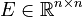 ,
,
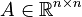 ,
,
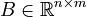 ,
,
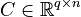 ,
,
 ,
,
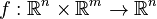 .
.
Nonlinear Time-Invariant Second-Order System (NLTI-SOS)
with
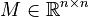 ,
,
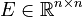 ,
,
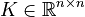 ,
,
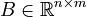 ,
,
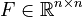 ,
,
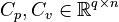 ,
,
 ,
,
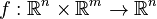 .
.
When 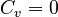 , we denote
, we denote 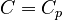 .
.