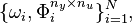| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
month = {February}, |
month = {February}, |
||
year = {2018}, |
year = {2018}, |
||
| − | pages = {}, |
+ | pages = {559-564}, |
} |
} |
||
| − | |||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 14:18, 28 January 2021
 Note: This page has not been verified by our editors.
Note: This page has not been verified by our editors.
Description
Motivation
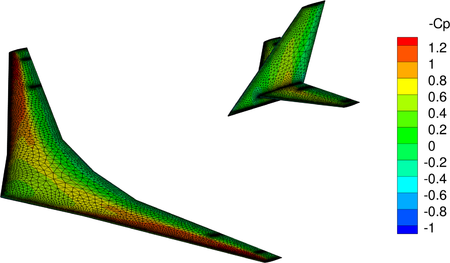
Flexible aircraft models are very challenging in civil aeronautics due to their lighter structure. Models are largely used by engineers to optimize and analyze critical phenomena in the pre-design phase. Such models can be used to monitor some dimensioning critical stress of the aircraft in response to discrete and continuous gust situations.
Computing responses to discrete gusts are sizing steps when designing and optimizing a new aircraft structure and geometry. Indeed, this is part of the imposed clearance certifications requested by the flight authorities. During the aircraft preliminary design phase, this clearance is done by intensive simulations. However, due to the involved model's complexity, these latter are time-consuming and imply an important computational burden. Moreover, these simulations are involved at different steps of the aircraft optimization process, by aeroelastic, flight and control engineers.
In [1], a systematic way to fasten the gust simulation step and simplify the analysis by mean of data-driven model approximation in the Loewner framework is proposed, as well as a description of this model.
Considered data
This benchmark contains a set of frequency-domain input-output data computed from a high fidelity simulator, and given as the couple
where 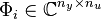 represents the transfer from
represents the transfer from 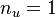 input signal (gust disturbance) to
input signal (gust disturbance) to 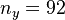 measurement outputs (accelerations and moments at different coordinates of a flexible aircraft wings and tail ), evaluated at varying frequencies
measurement outputs (accelerations and moments at different coordinates of a flexible aircraft wings and tail ), evaluated at varying frequencies 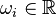 [rad/s], for
[rad/s], for 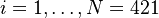 .
.
Origin
Collaboration between ONERA and DLR.
Data
The FlexibleAircraft.zip (585KB) repository contains two files:
- The dataONERA_FlexibleAircraft.mat data file, with
- W : the frequency values in rad/s (real
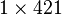 vector).
vector). - H : transfer function matrix evaluation at different output measurements points of the aircraft (complex
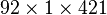 matrix).
matrix).
- W : the frequency values in rad/s (real
- The startONERA_FlexibleAircraft.m script file, used to loads and plots the data for illustration.
The transfer function matrix represents the transfer from the gust input to the 92 measurements gathering from
- 1--44: the local aerodynamic lift on the aerodynamic strips.
- 45--88: the local aerodynamic pitch moment on the aerodynamic strips.
- 89--92: the four generalized coordinates derivative (heave and pitch derivatives) and the first two flexible modes.
Citation
To cite this benchmark, use the following references:
- For the benchmark itself and its data:
- The MORwiki Community, Flexible AIrcraft. MORwiki - Model Order Reduction Wiki, 2018. https://morwiki.mpi-magdeburg.mpg.de/morwiki/index.php/Flexible_Aircraft
@inproceedings{PoussotMATHMOD:2018,
author = {C. Poussot-Vassal and D. Quero and P. Vuillemin},
title = {Data-driven approximation of a high fidelity gust-oriented flexible aircraft dynamical model},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IFAC Mathematical Modelling},
address = {Vienna, Austria},
month = {February},
year = {2018},
pages = {559-564},
}
References
- ↑ C. Poussot-Vassal, D. Quero, and P. Vuillemin, "Data-driven approximation of a high fidelity gust-oriented flexible aircraft dynamical model", in Proceedings of the 9th Vienna International Conference on Mathematical Modelling (MATHMOD), Vienna, Austria, 2018, pp 559-564, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.03.094.