| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The FitzHugh-Nagumo system describes a prototype of an excitable system (e.g., a neuron). |
The FitzHugh-Nagumo system describes a prototype of an excitable system (e.g., a neuron). |
||
If the external stimulus <math>i_0(t)</math> exceeds a certain threshold value, the system will exhibit a characteristic excursion in phase space, before the variables <math>v</math> and <math>w</math> relax back to their rest values. This behaviour is typical for spike generations (=short elevation of membrane voltage <math>v</math>) in a neuron after stimulation by an external input current. |
If the external stimulus <math>i_0(t)</math> exceeds a certain threshold value, the system will exhibit a characteristic excursion in phase space, before the variables <math>v</math> and <math>w</math> relax back to their rest values. This behaviour is typical for spike generations (=short elevation of membrane voltage <math>v</math>) in a neuron after stimulation by an external input current. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Here, we present the setting from [1], where the equations for the dynamical system read |
||
| + | |||
| + | <math> |
||
| + | \epsilon v_t(x,t)=\epsilon^2v_{xx}(x,t)+f(v(x,t))-w(x,t)+g, \\ |
||
| + | </math> |
||
| + | |||
| + | <math> |
||
| + | w_t(x,t)=hv(x,t)-\gamma w(x,t)+g, |
||
| + | </math> |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 16:21, 20 November 2012
Description
The FitzHugh-Nagumo system describes a prototype of an excitable system (e.g., a neuron).
If the external stimulus 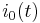 exceeds a certain threshold value, the system will exhibit a characteristic excursion in phase space, before the variables
exceeds a certain threshold value, the system will exhibit a characteristic excursion in phase space, before the variables  and
and 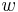 relax back to their rest values. This behaviour is typical for spike generations (=short elevation of membrane voltage
relax back to their rest values. This behaviour is typical for spike generations (=short elevation of membrane voltage  ) in a neuron after stimulation by an external input current.
) in a neuron after stimulation by an external input current.
Here, we present the setting from [1], where the equations for the dynamical system read
Failed to parse (syntax error): \epsilon v_t(x,t)=\epsilon^2v_{xx}(x,t)+f(v(x,t))-w(x,t)+g, \\
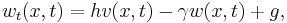
References
Contact information:
