m |
(include matlab source) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Usage== |
==Usage== |
||
| + | |||
| − | To generate a random system using the '''Inverse Lyapunov Procedure''' download the M-file [[Media:ilp.m|ilp.m]]. |
||
| + | Use the following matlab code to generate a random system by ilp: |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="matlab"> |
||
| + | |||
| + | function [A B C] = ilp(J,N,O,s) |
||
| + | % ilp (inverse lyapunov procedure) |
||
| + | % by Christian Himpe, 2013 ( http://gramian.de ) |
||
| + | % released under BSD 2-Clause License ( http://gramian.de/#license ) |
||
| + | %* |
||
| + | |||
| + | if(exist('emgr')~=2) disp('emgr framework is required. Download at http://gramian.de/emgr.m'); return; end |
||
| + | |||
| + | %% Gramian Eigenvalues |
||
| + | WC = exp(-N + N*rand(N,1)); |
||
| + | WO = exp(-N + N*rand(N,1)); |
||
| + | |||
| + | %% Gramian Eigenvectors |
||
| + | X = randn(N,N); |
||
| + | [U E V] = svd(X); |
||
| + | |||
| + | %% Balancing Trafo |
||
| + | [P D Q] = svd(diag(WC.*WO)); |
||
| + | W = -D; |
||
| + | |||
| + | %% Input and Output |
||
| + | B = randn(N,J); |
||
| + | |||
| + | if(nargin<4 || s==0) |
||
| + | C = randn(O,N); |
||
| + | else |
||
| + | C = B'; |
||
| + | end |
||
| + | |||
| + | %% Scale Output Matrix |
||
| + | BB = sum(B.*B,2); % = diag(B*B') |
||
| + | CC = sum(C.*C,1)'; % = diag(C'*C) |
||
| + | C = bsxfun(@times,C,sqrt(BB./CC)'); |
||
| + | |||
| + | %% Solve System Matrix |
||
| + | f = @(x,u,p) W*x+B*u; |
||
| + | g = @(x,u,p) C*x; |
||
| + | A = -emgr(f,g,[J N O],0,[0 0.01 1],'c'); |
||
| + | |||
| + | %% Unbalance System |
||
| + | T = U'*P'; |
||
| + | A = T*A*T'; |
||
| + | B = T*B; |
||
| + | C = C*T'; |
||
| + | |||
| + | </source> |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To download the M-file [[Media:ilp.m.tar.gz|ilp.m]]. |
||
The function call requires three parameters; the number of inputs <math>J</math>, of states <math>N</math> and outputs <math>O</math>. |
The function call requires three parameters; the number of inputs <math>J</math>, of states <math>N</math> and outputs <math>O</math>. |
||
Optionally, a symmetric system can be enforced with the parameter <math>s=1</math>. |
Optionally, a symmetric system can be enforced with the parameter <math>s=1</math>. |
||
Revision as of 16:06, 22 May 2013
Description
The Inverse Lyapunov Procedure (ilp) is a synthetic random linear system generator. It is based on reversing the Balanced Truncation procedure and was developed in [1], where a description of the algorithm is given.
A central point is the solution of the Lyapunov equations for the system matrix instead of the gramian matrix. This is feasable due to the symmetric (semi-)positive definiteness of the gramians and the requirement of a stable system. The solution will not be unique and include a symmetric system matrix, yet can be solved efficiently using empirical gramians.
Usage
Use the following matlab code to generate a random system by ilp:
function [A B C] = ilp(J,N,O,s)
% ilp (inverse lyapunov procedure)
% by Christian Himpe, 2013 ( http://gramian.de )
% released under BSD 2-Clause License ( http://gramian.de/#license )
%*
if(exist('emgr')~=2) disp('emgr framework is required. Download at http://gramian.de/emgr.m'); return; end
%% Gramian Eigenvalues
WC = exp(-N + N*rand(N,1));
WO = exp(-N + N*rand(N,1));
%% Gramian Eigenvectors
X = randn(N,N);
[U E V] = svd(X);
%% Balancing Trafo
[P D Q] = svd(diag(WC.*WO));
W = -D;
%% Input and Output
B = randn(N,J);
if(nargin<4 || s==0)
C = randn(O,N);
else
C = B';
end
%% Scale Output Matrix
BB = sum(B.*B,2); % = diag(B*B')
CC = sum(C.*C,1)'; % = diag(C'*C)
C = bsxfun(@times,C,sqrt(BB./CC)');
%% Solve System Matrix
f = @(x,u,p) W*x+B*u;
g = @(x,u,p) C*x;
A = -emgr(f,g,[J N O],0,[0 0.01 1],'c');
%% Unbalance System
T = U'*P';
A = T*A*T';
B = T*B;
C = C*T';
To download the M-file ilp.m.
The function call requires three parameters; the number of inputs 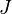 , of states
, of states  and outputs
and outputs 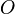 .
Optionally, a symmetric system can be enforced with the parameter
.
Optionally, a symmetric system can be enforced with the parameter 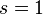 .
The return value consists of three matrices; the system matrix
.
The return value consists of three matrices; the system matrix  , the input matrix
, the input matrix  and the output matrix
and the output matrix  .
.
[A,B,C] = ilp(J,N,O,s);
The required Empirical Gramian Framework can be obtained from http://gramian.de. The ilp generator is compatible with MATLAB and OCTAVE.
References
- ↑ S.C. Smith, J. Fisher, "On generating random systems: a gramian approach", Proceedings of the American Control Conference, 2003.
