Note: This page has not been verified by our editors.
Note: This page has not been verified by our editors.
| Background | |
|---|---|
| Benchmark ID |
soundTransmission_n95480m1q1 |
| Category |
misc |
| System-Class |
LTI-SOS |
| Parameters | |
| nstates |
95480
|
| ninputs |
1 |
| noutputs |
1 |
| nparameters |
0 |
| components |
B, C, E, K, M |
| Copyright | |
| License |
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International |
| Creator | |
| Editor | |
| Location | |
|
https://zenodo.org/record/7670587/files/soundTransmission_n95480m1q1.mat | |
Description
The Sound transmission through a plate benchmark models the radiation of a vibrating plate and the excitation of a structure by an oscillating acoustic fluid. It is based on an experiment by Guy[1].
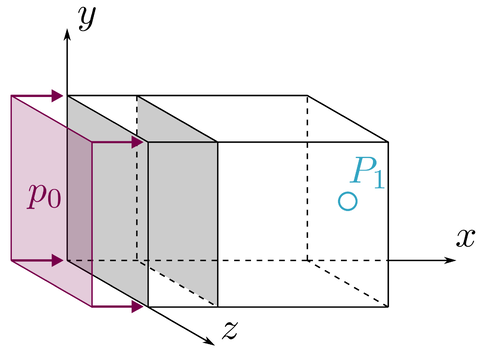
The system consists of a cuboid acoustic cavity, where one wall is considered a system of two parallel elastic brass plates with a \(2\,\mathrm{cm}\) air gap between them; all other walls are considered rigid. The plates measure \(0.2 \times 0.2\,\mathrm{m}\) and have a thickness of \(t = 0.9144\,\mathrm{mm}\); the receiving cavity is \(0.2\,\mathrm{m}\) wide. The outer plate is excited by a uniform pressure load and the resulting acoustic pressure in the receiving cavity is measured at the middle of the rigid wall opposite to the elastic plate (\(P_1\) in the sketch).
The following material parameters have been considered for the brass plates and the acoustic fluid:
| Part | Parameter | Value | Unit |
| Brass plates | \(E\) | \(104\) | \(\mathrm{GPa}\) |
| \(\rho\) | \(8500\) | \(\mathrm{kg}\,\mathrm{m}^{-3}\) | |
| \(\nu\) | \(0.37\) | \(-\) | |
| Acoustic fluid | \(c\) | \(343\) | \(\mathrm{m}\,\mathrm{s}^{-1}\) |
| \( \rho\) | \( 1.21\) | \( \mathrm{kg}\,\mathrm{m}^{-3}\) |
Dimensions
System structure:
\[ \begin{align} M \ddot{x}(t) + E \dot{x}(t) + K x(t) &= B u(t), \\ y(t) &= C x(t) \end{align} \]
System dimensions\[M \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\], \(E \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\), \(K \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\), \(B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times 1}\), \(C \in \mathbb{R}^{1 \times n}\), with \(n=95\,480\).
Proportional damping, i.e. \(E=\alpha M + \beta K\), with \(\alpha=0, \beta=1\cdot 10^{-7}\) is considered. The two-way coupling between the structure and the acoustic fluid results in non-symmetric matrices \(M, E, K\).
Data
The data is available at Zenodo.
Remarks
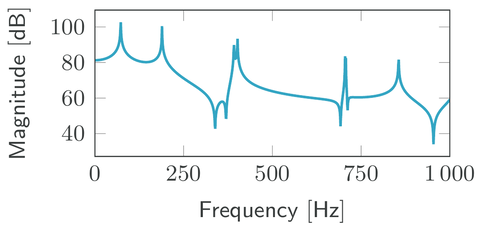
- The numerical model resembles the experimental data[1] in a frequency range from \(1\,\mathrm{Hz}\) to \(1000\,\mathrm{Hz}\). The frequency response in this range is also included in the dataset.
- The finite element discretization has been performed with Kratos Multiphysics.
- The system has unstable eigenvalues. This is common in interior acoustic problems where no damping is assumed for the acoustic fluid[2].
- A comparison of different interpolation-based MOR methods using this benchmark example is available in[3]
Citation
To cite this benchmark, use the following references:
- For the benchmark itself and its data:
@Misc{dataAum22,
author = {Aumann, Q.},
title = {Matrices for a sound transmission problem},
howpublished = {hosted at {MORwiki} -- Model Order Reduction Wiki},
year = 2022,
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.7300346}
}
- For the background on the benchmark:
@Article{AumW23,
author = {Aumann, Q. and Werner, S.~W.~R.},
title = {Structured model order reduction for vibro-acoustic problems using interpolation and balancing methods},
journal = {Journal of Sound and Vibration},
volume = 543,
year = 2023,
pages = {117363},
doi = {10.1016/j.jsv.2022.117363},
publisher = {Elsevier {BV}}
}
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 R. W. Guy. "The Transmission of Airborne Sound through a Finite Panel, Air Gap, Panel and Cavity Configuration – a Steady State Analysis ", Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 49(4): 323--333, 1981.
- ↑ V. Cool, S. Jonckheere, E. Deckers, W. Desmet. "Black box stability preserving reduction techniques in the Loewner framework for the efficient time domain simulation of dynamical systems with damping treatments", Journal of Sound and Vibration, 529: 116922, 2022.
- ↑ Q. Aumann, S. W. R. Werner. "Structured model order reduction for vibro-acoustic problems using interpolation and balancing methods", Journal of Sound and Vibration, 543: 117363, 2023.